Waterfall Model
It is a linear-sequential life cycle model. It is very simple to understand and use. In a waterfall model, each phase must be completed fully before the next phase can begin. This type of software development model is basically used for the project which is small and there are no uncertain requirements.
Waterfall is a sequential approach that divides the SDLC to distinct phases such as requirements gathering, analysis and design, coding and unit testing, system and user acceptance testing, and deployment. The next phase can only proceed if the previous phase has been completed. In between phases, a deliverable is expected or a document is signed off.
All phases are passed through and completed only once, so all requirements are gathered as much as possible at the start to provide the information in creating the plans, schedules, budget, and resources. It is plan-driven, so any changes after the project has started would offset the original plan and require a restart.
In this model software testing starts only after the development is complete. In waterfall model phases do not overlap.
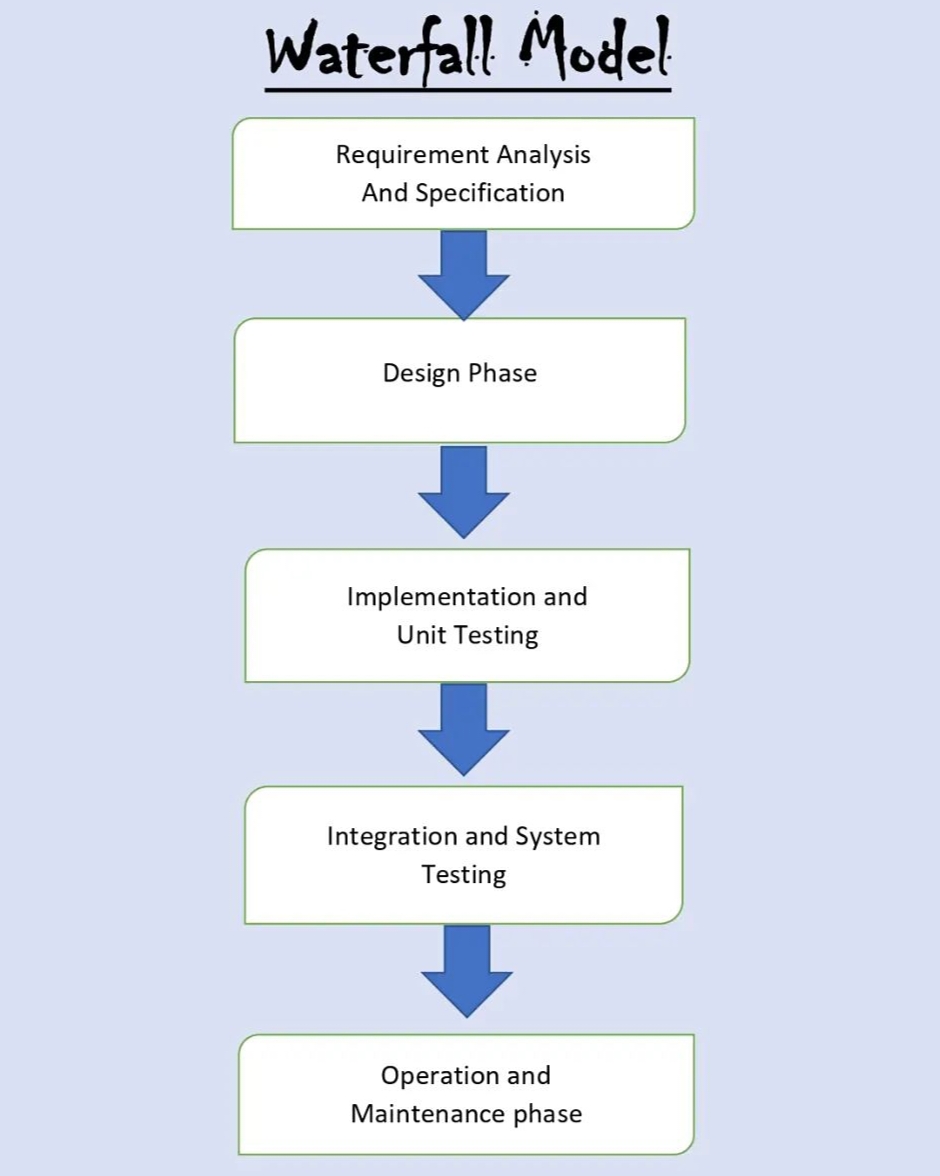
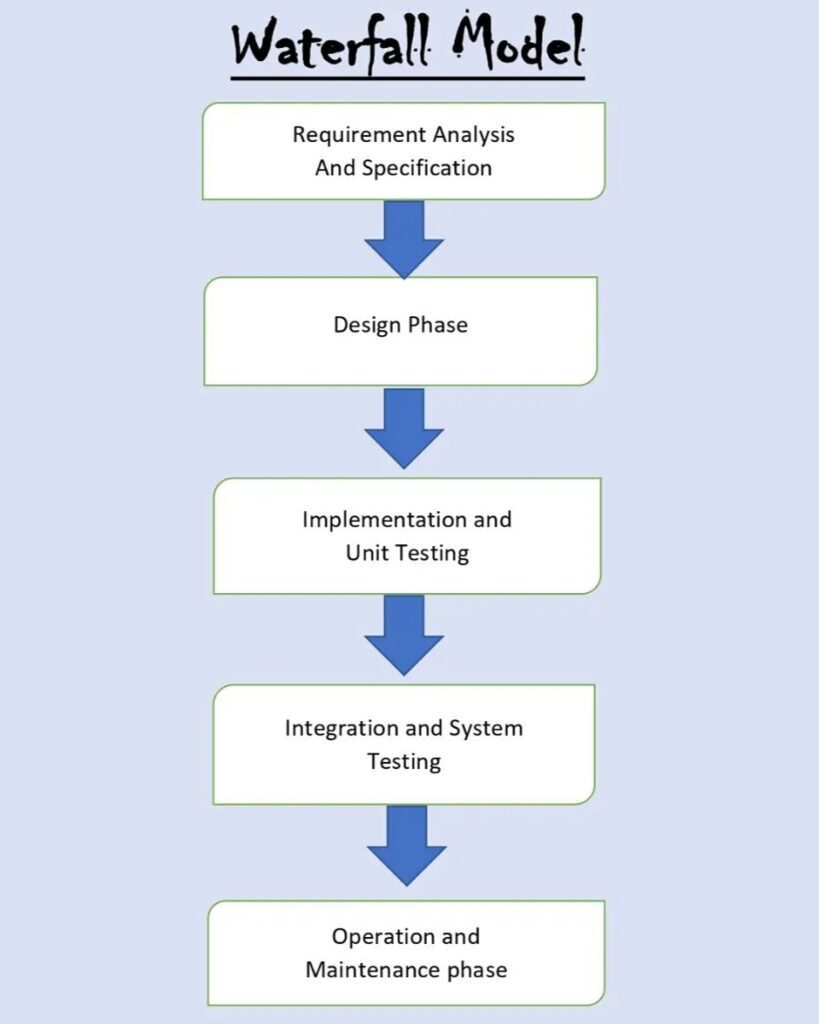
Phases of Waterfall Model
Requirements Gathering and Analysis
In this phase the requirements are gathered by the business analyst and they are analyzed by the team. Requirements are documented during this phase and clarifications can be sought.
The Business Analysts document the requirement based on their discussion with the customer.
System Design
The architect and senior members of the team work on the software architecture, high level and low level design for the project.
The requirement specifications from the first phase are studied in this phase and system design is prepared. System Design helps in specifying hardware and system requirements and also helps in defining overall system architecture
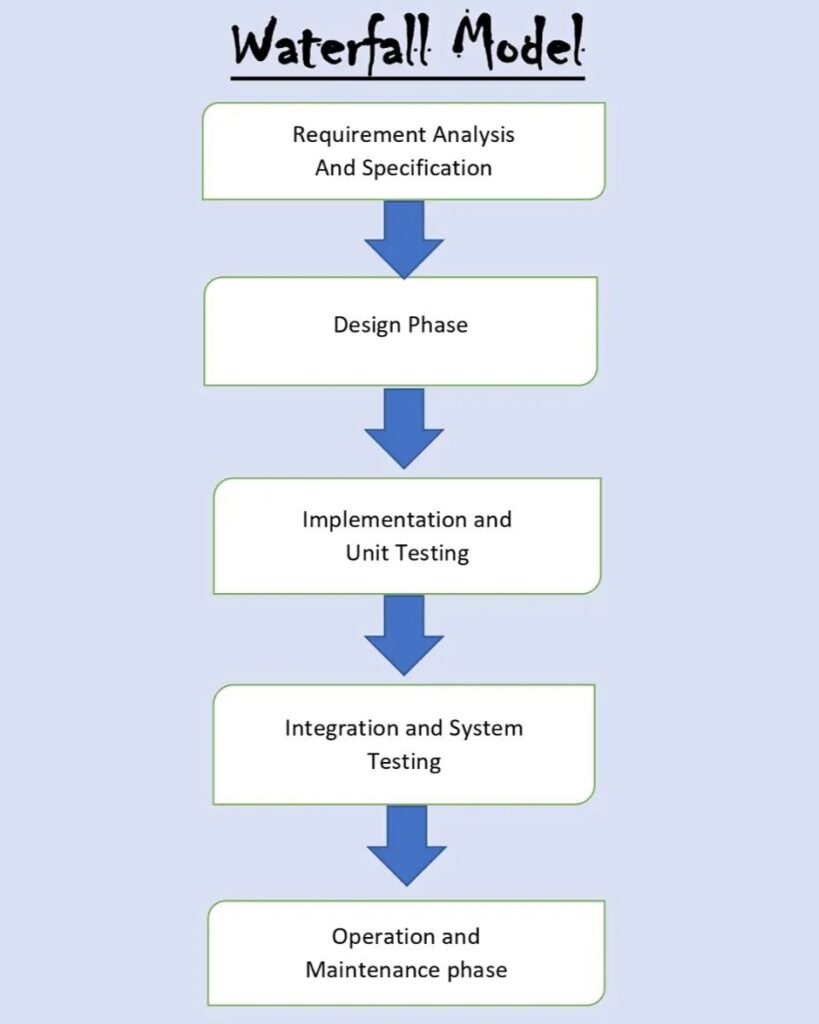
Development/ Implementation
The development team works on coding the project.
They take the design documents / artifacts and ensure that their solution follows the design finalized by the architect.
With inputs from system design, the system is first developed in small programs called units, which are integrated into the next phase. Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality which is referred to as Unit Testing.
Testing
The testing team tests the complete application and identifies any defects in the application.
These defects are fixed by the developers and the testing team tests the fixes to ensure that the defect is fixed.
They also perform regression testing of the application to see if any new defects were introduced.
Deployment
The team builds and installs the application on the servers which were procured for the banking application.
Some of the high level activities include installing the OS on the servers, installing security patches, hardening the servers, installing web servers and application servers, installing the database etc.
They also coordinate with network and IT administrative teams etc to finally get the application up and running on the production servers.
Once the functional and non-functional testing is done, the product is deployed in the customer environment or released into the market.
Maintenance
During the maintenance phase, the team ensures that the application is running smoothly on the servers without any downtime.
Issues that are reported after going live are fixed by the team and tested by the testing team.
This step occurs after installation, and involves making modifications to the system or an individual component to alter attributes or improve performance. These modifications arise either due to change requests initiated by the customer, or defects uncovered during live use of the system. The client is provided with regular maintenance and support for the developed software.
Examples of Waterfall Model
In the olden days, Waterfall model was used to develop enterprise applications like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS), Supply Chain Management Systems, Inventory Management Systems, Point of Sales (POS) systems for Retail chains etc.
Another ex, waterfall model can be used in developing a simple calculator as the functions of addition, subtraction etc and the numbers will not change for a long time.
These days most project follow Agile Methodology, some form of Iterative model or one of the other models depending on their project specific requirement.
Advantages of waterfall model
- This model is simple and easy to understand and use.
- requirements do not change nor does design and code, so we get a stable product.
- In this model phases are processed and completed one at a time. Phases do not overlap.
- Waterfall model works well for smaller projects where requirements are clearly defined and very well understood.
Disadvantages of Waterfall model
- Design is not adaptive; often when a flaw is found, the entire process needs to start over.
- Once an application is in the testing stage, it is very difficult to go back and change something that was not well-thought out in the concept stage.
- High amounts of risk and uncertainty
- Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects.
- Poor model for long and ongoing projects.
When to use the waterfall model
- This model is used only when the requirements are very well known OR freezed, clear and fixed.
- Product definition is stable.
- The project is short.
In the Waterfall model, very less customer interaction is involved during the development of the product. Once the product is ready then only it can be demonstrated to the end users.
Once the product is developed and if any failure occurs then the cost of fixing such issues are very high, because we need to update everything from document till the logic.
In today’s world, the Waterfall model has been replaced by other models like iterative, agile etc.
Difference between: Waterfall Model vs Agile Model
| Waterfall model | Agile Model |
| Planning – Waterfall model requires planning for long term which requires complete clarity in requirements | Planning in Agile projects is generally on a short term since the work product is delivered in 2 to 4 weeks |
| Waterfall avoids scope changes once the project starts | Agile allows requirement changes at any time |
| Sequential planning with clearly defined milestone details and predictability are characteristics of Waterfall projects | Planning in Agile projects is iterative in nature and adapts to changing requirement |
| testing phase comes only after the build phase in a Waterfall project | Testing is performed concurrently with development in Agile |
| Waterfall is a linear and sequential approach | Agile is an incremental and iterative approach |
| Waterfall divides a project into phases | Agile separates a project into sprints |
| Waterfall helps complete one single project | Agile helps complete many small projects |
| Waterfall focuses on successful project delivery | Agile introduces a product mindset with a focus on customer satisfaction |
| test teams in Waterfall do not get involved in requirements change | Test teams in Agile can take part in requirements change |
More Update Join WhatsApp Group :- Apply Here